문제 링크 : https://leetcode.com/problems/combination-sum/
Combination Sum - LeetCode
Level up your coding skills and quickly land a job. This is the best place to expand your knowledge and get prepared for your next interview.
leetcode.com
유형 : 백트래킹(BackTracking)
문제 설명
중복되지 않는 정수들이 담긴 배열 candidates와 정수 target이 주어질 때, candidates에서 선택한 숫자들의 합이 target이 되는 조합을 찾아 모두 return 하는 문제이다. 이때, candidates의 숫자를 여러 번 사용하여 조합을 구성할 수 있다. 또한 [2,2,3]과 [3,2,2]는 동일한 조합으로 한 번만 return 해야 한다.
Example 1)
Input: candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7
Output: [[2,2,3],[7]]
Example 2)
Input: candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8
Output: [[2,2,2,2],[2,3,3],[3,5]]
Example 3)
Input: candidates = [2], target = 1
Output: []
제한사항
- 1 <= candidates.length <= 30
- 1 <= candidates[i] <= 200
- candidates의 모든 숫자들은 중복되지 않는다.
- 1 <= target <= 500
문제 풀이
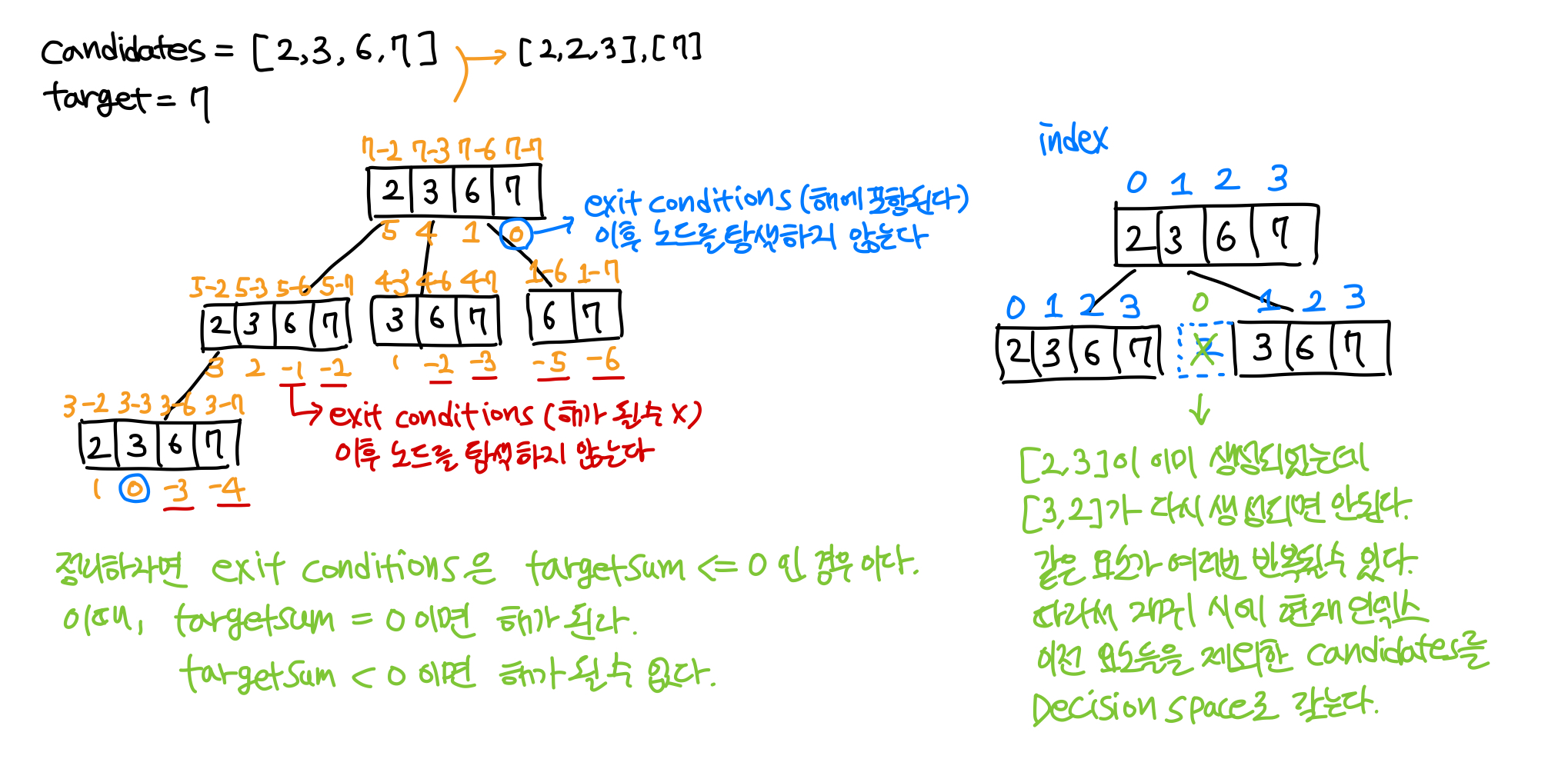
성공 코드
from typing import List
class Solution:
def combinationSum(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
self.candidates = candidates
self.target = target
self.combs = []
self.bt(0, target, [])
return self.combs
def bt(self, prevIdx: int, targetSum: int, comb:List[int]):
# exit conditions
if targetSum == 0:
self.combs.append(comb.copy())
return
elif targetSum < 0:
return
# process(candidates filtering)
for idx in range(prevIdx, len(self.candidates)):
num = self.candidates[idx]
# recursion call
comb.append(num)
self.bt(idx, targetSum-num, comb)
comb.pop()시간복잡도 : T(n) <= n^(target/m + 1)
m은 후보들 중 가장 작은 수를 의미한다.
공간복잡도 : O(target/m)
m은 후보들 중 가장 작은 수를 의미한다.